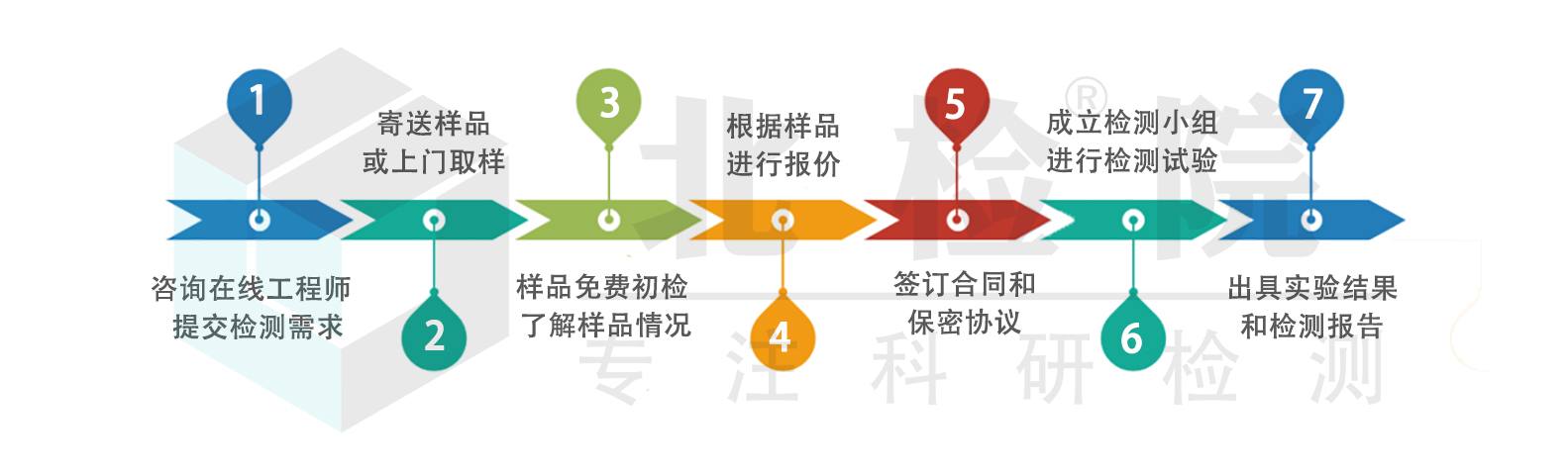
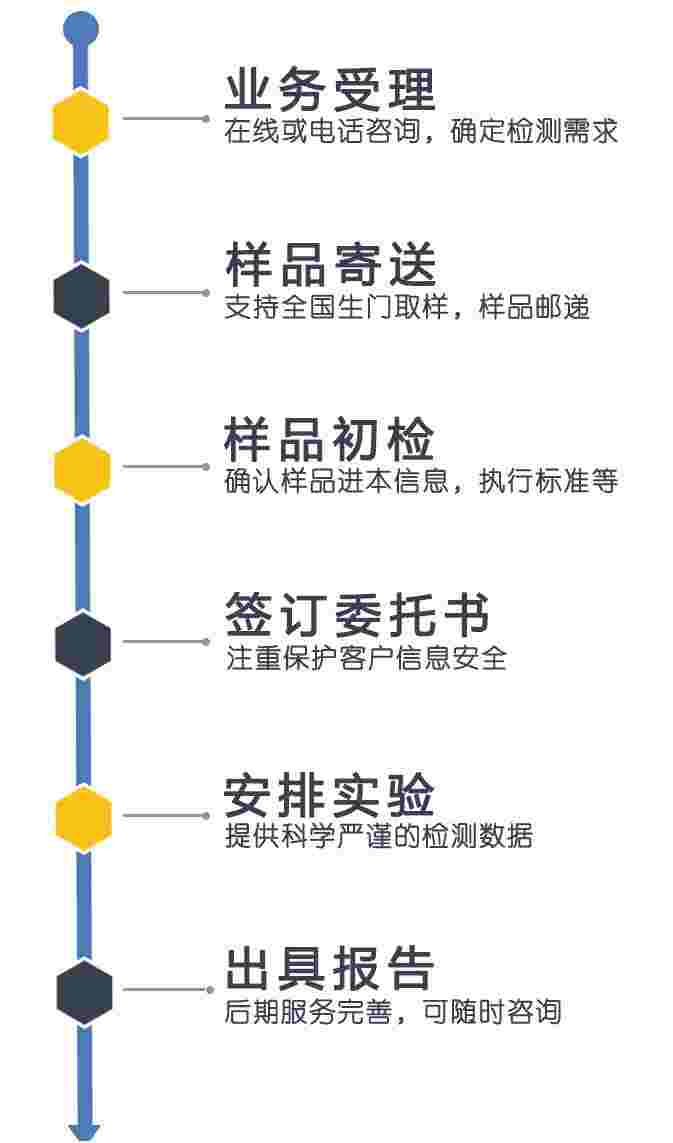
注意:因业务调整,暂不接受个人委托测试,望见谅。
检测项目(部分)
三氧化二铁
氧化镁
氧化钾和氧化钠
三氧化二铝
二氧化硅
氧化钙
烧失量
检测样品(部分)
建材用石灰石、生石灰和熟石灰
检测标准(部分)
These test methods provide accurate and reliable analytical procedures to determine the chemical constituents of limestone quicklime and hydrated lime (See Note 1). The percentages of specific constituents which determine a materialrsquo;quality or fitness for use are of significance depending upon the purpose or end use of the material. Results obtained may be used in relation to specification requirements.
Because quicklime and hydrated lime quickly absorb water and carbon dioxide from the air precision and bias are extremely dependent upon precautions taken during sample preparation and analysis to minimize excessive exposure to ambient conditions.
Note 18212;These test methods can be applied to other calcareous materials if provisions are made to compensate for known interferences.
1.1 These test methods cover the chemical analysis of high-calcium and dolomitic limestone quicklime and hydrated lime. These test methods are classified as either standard (preferred) or alternative (optional).
1.2 The standard test methods are those that employ classical gravimetric or volumetric analytical procedures and are typically those required for referee analyses where chemical specification requirements are an essential part of contractual agreement between buyer and seller.
1.3 Alternative or optional test methods are provided for those who wish to use procedures shorter or more convenient than the standard methods for the routine determinations of certain constituents. Optional test methods may sometimes be preferred to the standard test methods but frequently the use of modern and expensive instrumentation is indicated which may not be accessible to everyone. Therefore the use of these test methods must be left to the discretion of each laboratory.
1.4 The analytical procedures appear in the following order:
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns if any associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific precautionary statements see and .
1.1 These test methods cover the chemical analysis of high-calcium and dolomitic limestone quicklime and hydrated lime. These test methods are classified as either standard (preferred) or alternative (optional).
1.2 The standard test methods are those that employ classical gravimetric or volumetric analytical procedures and are typically those required for referee analyses where chemical specification requirements are an essential part of contractual agreement between buyer and seller.
1.3 Alternative or optional test methods are provided for those who wish to use procedures shorter or more convenient than the standard methods for the routine determinations of certain constituents. Optional test methods may sometimes be preferred to the standard test methods but frequently the use of modern and expensive instrumentation is indicated which may not be accessible to everyone. Therefore the use of these test methods must be left to the discretion of each laboratory.
1.4 The analytical procedures appear in the following order:
Section Aluminum Oxide 15 Available Lime Index 28 Calcium and Magnesium Oxide: Alternative EDTA Titration Method 31 Calcium Carbonate Equivalent 33 Calcium Oxide: Gravimetric Method 16 Volumetric Method 17 Carbon Dioxide by Standard Method 22 Combined Oxides of Iron and Aluminum 12 Ferrous Iron X5 Free Calcium Oxide X6 Free Moisture in Hydrated Lime 21 Free Moisture in Limestone 20 Free Silica 29 Insoluble Matter Including Silicon Dioxide: Standard Method 8 Optional Perchloric Acid Method 9 Insoluble Matter Other Than Silicon Dioxide 11 Loss on Ignition 19 Magnesium Oxide 18 Manganese: Bismuthate Method X4 Periodate (Photometric) Method 27 pH Determination of Alkaline Earth Solutions 34 1a Phosphorus: Titrimetric Method X3 Molybdovanadate Method 26 Silicon Dioxide 10 Strontium Oxide X2 Sulfur Trioxide 23 Total Carbon: Direct Combustion-Thermal Conductivity Cell Method 32 Total Iron: Standard Method Potassium Dichromate Titration 13 Potassium Permanganate Titration Method X1 Ortho-Phenanthroline Photometric Method 14 Total Sulfur: Sodium Carbonate Fusion 24 Combustion-Iodate Titration Method 25 Unhydrated Oxides 301.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns if any associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific precautionary statements see Notes 11 13 27 47 X2.1 and X5.1.
1.1 These test methods cover physical testing of quicklime and hydrated lime and of limestone not otherwise covered in ASTM standards.
Note 18212;Quicklime and hydrated lime have a high affinity for moisture and carbon dioxide. Caution should be taken to protect both hydrated and quicklime during sampling storage and testing (see Practice C50).
1.1 These test methods cover physical testing of quicklime and hydrated lime and of limestone not otherwise covered in ASTM standards. Note 1Quicklime and hydrated lime have a high affinity for moisture and carbon dioxide. Caution should be taken to protect both hydrated and quicklime during sampling storage and testing (see Practice C 50).
1.2 The test procedures appear in the following order:
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns if any associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.1 This specification covers high calcium dolomitic and magnesian-hydrated lime for use in asphalt cement or bituminous pavement.
Note 1Hydrated lime either calcitic dolomitic or magnesian improves bonding of bitumen and aggregates which reduces susceptibility to moisture damage reduces age hardening by chemically stabilizing polar compounds found in asphalts and increases initial stiffness of asphalt mixtures.
Note 2No attempt is made to present requirements for any by-product lime.
This standard does not purport to address the safety concerns associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.1 This specification covers lime and limestone products suitable for chemical uses as shown in . The type designations signify the following:
| Limestone high-calcium-CL |
| Limestone dolomitic-DL |
| Limestone magnesian-ML |
| Quicklime high-calcium-CQ |
| Quicklime dolomitic-DQ |
| Quicklime magnesian-MQ |
| Hydrated lime high-calcium-CH |
| Hydrated lime dolomitic-DH |
| Hydrated lime magnesian-MH |
| Hydrated lime by-product-BH |
Note 18212;Lime is used in environmental systems when the control of factors influencing the environment such as gases liquids and solids is required.
<>1.2 The buyer shall designate the use as listed in Table 1 and may specify one or more of the type designations in 1.1.
1.1 This specification covers high calcium dolomitic and magnesian-hydrated lime for use in asphalt cement or bituminous paving mixtures.
Note 1: Hydrated lime either calcitic dolomitic or magnesian improves bonding of bitumen and aggregates which reduces susceptibility to moisture damage reduces age hardening by chemically stabilizing polar compounds found in asphalts and increases initial stiffness of asphalt mixtures.
Note 2: No attempt is made to present requirements for any by-product lime.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns if any associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety health and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT)
1.1 These test methods cover the chemical analysis of high-calcium and dolomitic limestone quicklime and hydrated lime. These test methods are classified as either standard (preferred) or alternative (optional).
1.2 The standard test methods are those that employ classical gravimetric or volumetric analytical procedures and are typically those required for referee analyses where chemical specification requirements are an essential part of contractual agreement between buyer and seller.
1.3 Alternative or optional test methods are provided for those who wish to use procedures shorter or more convenient than the standard methods for the routine determinations of certain constituents. Optional test methods may sometimes be preferred to the standard test methods but frequently the use of modern and expensive instrumentation is indicated which may not be accessible to everyone. Therefore the use of these test methods must be left to the discretion of each laboratory.
1.4 The analytical procedures appear in the following order: